- By Admin
- 江苏雨灵机械科技有限公司
-
Construct Ion
-
0 Comments
- Industry News
- 294
Plate Heat Exchangers: Structure, Applications, and Effective Cleaning Solutions
I. Basic Structure of Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers mainly consist of two parts: the frame and the plates.
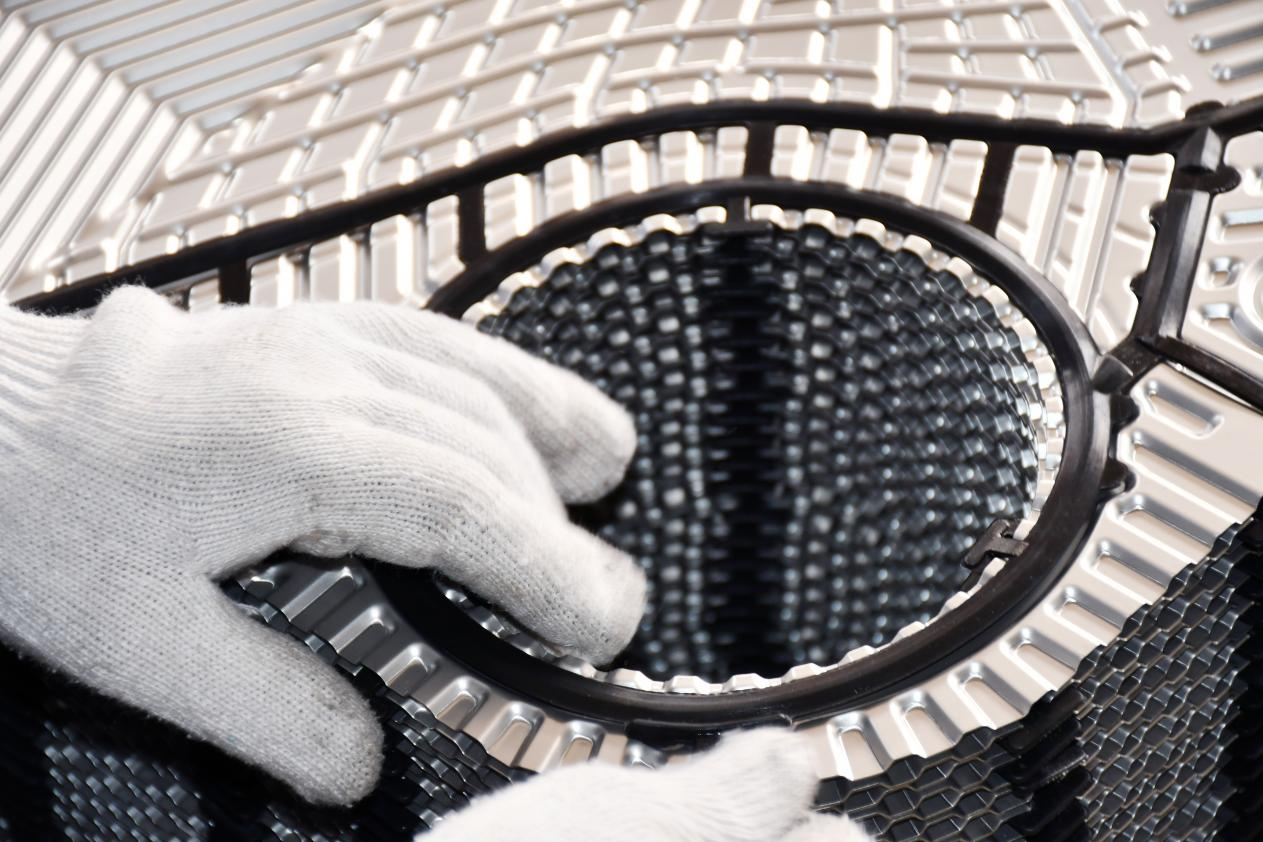
The plates are thin sheets made of various materials, pressed into different corrugated shapes using various molds. Corner holes are punched in the four corners of each plate to serve as flow channels for the media. The edges and corner holes of the plates are sealed with rubber gaskets.
The frame consists of a fixed pressure plate, a movable pressure plate, upper and lower guide rods, and clamping bolts.
The plate heat exchanger is assembled by stacking the plates between the fixed and movable pressure plates, and then clamping them together with clamping bolts.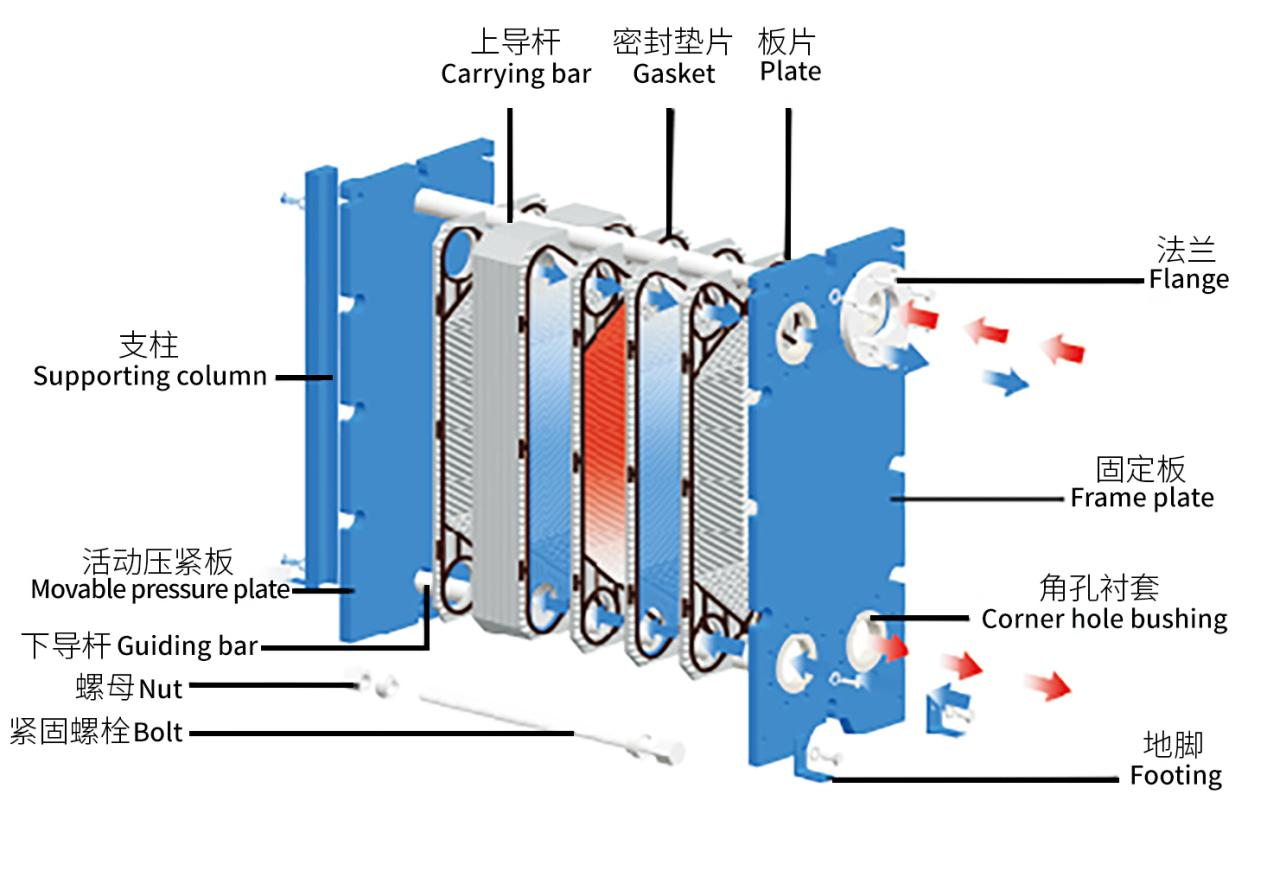
II.Applications of Plate Heat Exchangers:
a. Refrigeration: Used as condensers and evaporators.
b. HVAC: Intermediate heat exchangers used with boilers, intermediate heat exchangers in high-rise buildings, etc.
c. Chemical Industry: Soda ash industry, ammonia synthesis, alcohol fermentation, resin synthesis cooling, etc.
d. Metallurgical Industry: Heating or cooling of aluminate mother liquor, cooling in steelmaking processes, etc.
e. Mechanical Industry: Cooling of various quenching fluids, cooling of reducer lubricating oil, etc.
f. Power Industry: Cooling of high-voltage transformer oil, cooling of generator bearing oil, etc.
g. Paper Industry: Heat recovery in bleaching processes, heating of pulp washing liquid, etc.
h. Textile Industry: Cooling of viscose rayon alkaline solution, cooling of boiling nitrocellulose, etc.
i. Food Industry: Juice sterilization and cooling, heating and cooling of animal and vegetable oils, etc.
j. Oil and Fat Processing: Atmospheric drying of soap base, heating or cooling of various process liquids.
k. Central Heating: District heating using waste heat from power plants, heating of bath water.
l. Others: Petroleum, pharmaceuticals, shipbuilding, seawater desalination, geothermal energy utilization.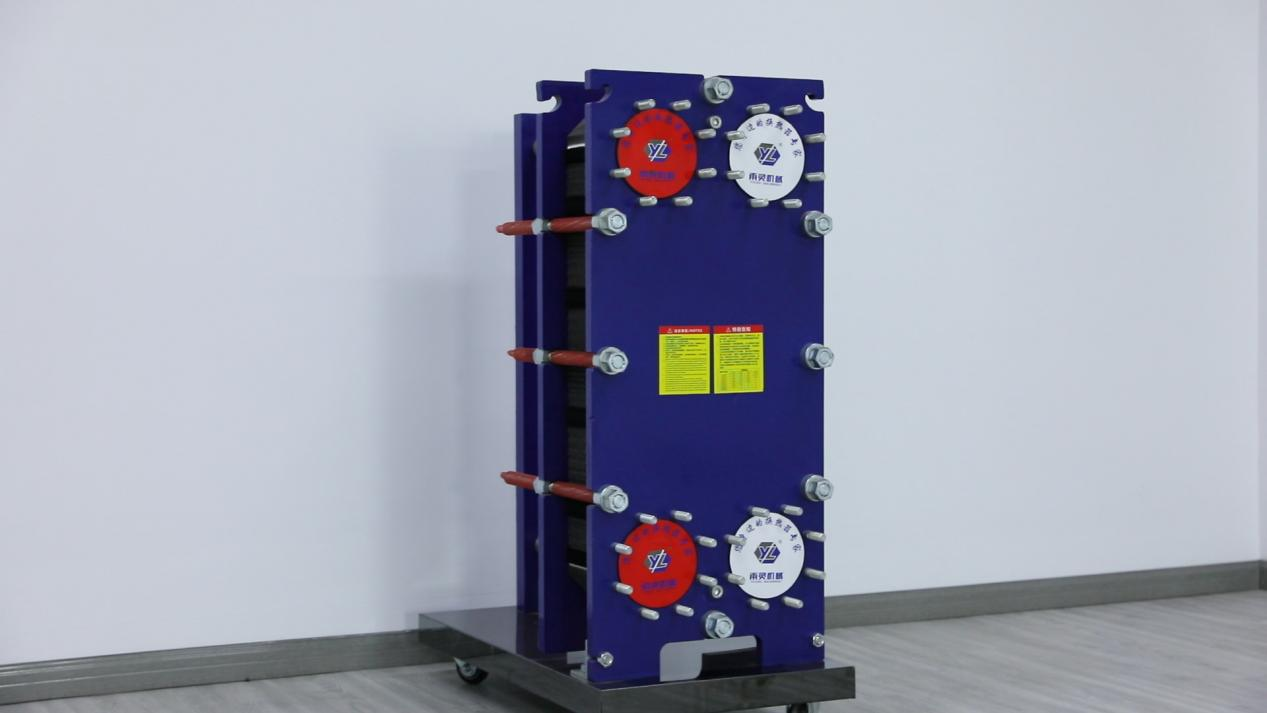
III.Main Causes and Hazards of Fouling and Blockage in Plate Heat Exchangers
During the operation of plate heat exchangers, improper operation of water treatment equipment and substandard water quality control can lead to the injection of unqualified softened water into the heating system. This causes calcium, magnesium, and carbonates in the water to decompose upon heating, forming calcium carbonate and magnesium hydroxide precipitates that adhere to the heat transfer surfaces of the exchanger, forming hard scale. Due to the poor thermal conductivity of this scale, the heat transfer efficiency of the exchanger is reduced, resulting in significant energy waste and negatively impacting heating performance. This causes serious adverse effects for heating companies.

IV. Selection of Cleaning Agents
Currently, acid cleaning is used, which includes both organic and inorganic acids. Organic acids mainly include oxalic acid and formic acid. Inorganic acids mainly include hydrochloric acid and nitric acid. Based on the analysis of heat exchanger scaling, process, materials, and scale composition, the following conclusions were drawn:
1) The heat exchanger has a small flow area and a complex internal structure, making it difficult to discharge cleaning solutions if precipitation occurs.
2) The heat exchanger material is a nickel-titanium alloy. Using hydrochloric acid as the cleaning solution can easily cause strong corrosion to the plates, shortening the service life of the heat exchanger.
Through repeated experiments, it was found that formic acid is the most effective cleaning solution. Adding buffering agents and surfactants to the formic acid cleaning solution further improves the cleaning effect and reduces the corrosion of the plates.
Chemical tests on scale samples showed that formic acid can effectively remove scale. Acid immersion tests revealed that formic acid effectively removes scale attached to the plates while causing minimal corrosion to the heat exchanger plates.

